
WHAT IS an MBA? KNOW ABOUT MBA
Master of Business Administration:
The Master of Business Administration (MBA Degree), commonly known as ‘MBA’, has its roots in the USA. At the start of the 20th century, when the country industrialized and companies required scientific and systematic approaches to business and management, the MBA was founded. The main courses in an MBA degree cover various areas of business, such as accounting, business ethics, business law, finance, managerial economics, management, entrepreneurship, statistics, marketing management, sales, business communication, supply chain, and operations management in a manner most relevant to business analysis and strategy.

An MBA degree includes elective courses and concentrations for deep study in a particular area, for example, accounting, finance, and marketing. The degrees offered by UGC or PGDM approved by AICTE in India typically require completing about 120 credits. Wherein one credit means 10 hours of study.
The MBA program is more about networking and skill development. Regulating bodies specifically for the Master of Business Administration program ensure consistency and quality of education across colleges and universities. Universities in many countries offer programs tailored to full-time, part-time, executive, distance learning programs, and online Master of Business Administration, many with specialized areas.
The very first Business School in the USA was The Wharton School, established in 1881, under the University of Pennsylvania. In 1900, the Tuck School of Business was established at Dartmouth College, conferring the first advanced degree in management, specifically, an M.Sc. in Commerce, the predecessor to the Master of Business Administration.
The Harvard Business School commenced the first Master of Business Administration (MBA) course in 1908, having 15 professors, 33 regular students & 47 other students.
Important Dates include:
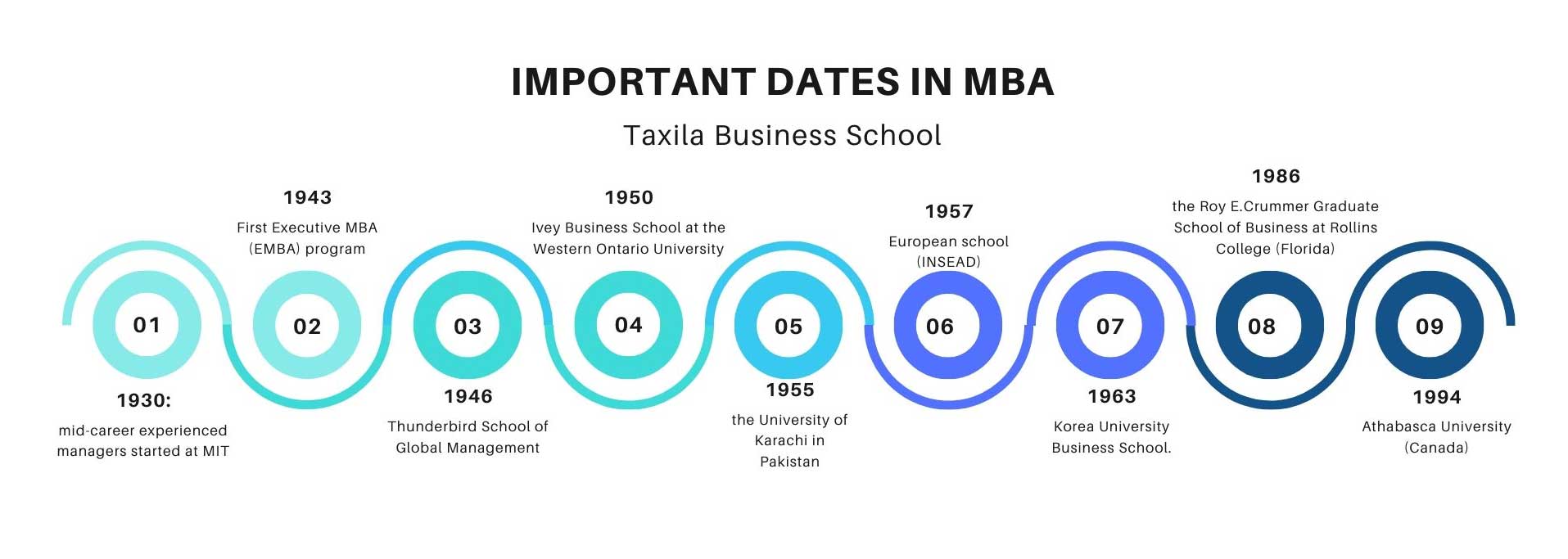
- 1930: The First management and leadership Executive education program for executives and mid-career experienced managers started at MIT.
- 1943: First Executive MBA (EMBA) program for working people at the University of Chicago, Booth School of Business. Chicago was among the first business schools to have permanent campuses on three continents in Chicago (USA), Barcelona (Europe), and Singapore (Asia).
- 1946: 1st Master of Business Administration program focused on global management was started at Thunderbird School of Global Management.
- 1950: 1st MBA outside of the US, in Canada (Ivey Business School at Western Ontario University), preceded by the University of Pretoria in South Africa in 1951.
- 1955: 1st MBA offered at an Asian school at the Institute of Business Administration Karachi at the University of Karachi in Pakistan, in collaboration with the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania.
- 1957: 1st Master of Business Administration course offered at a European school (INSEAD).
- 1963: 1st MBA course offered in Korea by Korea University Business School.
- 1986: 1st Master of Business Administration course requiring all the students to have a laptop in the classroom at the Roy E.Crummer Graduate School of Business at Rollins College (Florida).
- 1994: 1st online executive MBA degree at Athabasca University (Canada).
The degree has now been adopted by universities across the world in all countries.
Accreditation:

United States
For MBA/PGDM, a few external agencies provide students and employers with an unbiased view of the school or the syllabus quality, as well as whether the syllabus meets international quality standards. The three main accrediting agencies in the United States are:
- AACSB (Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business in the United States of America).
- ACBSP (Accreditation Council for Business Schools and Programs).
- IACBE (International Assembly for Collegiate Business Education).
These agencies also accredit Business Schools outside the USA.
India:
Agencies outside of the USA that accredit MBA include AMBA (Association of MBAs), a British-based company that accredits MBA/PGDM, and the Central government approval bodies, such as the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE), which approves Master of Business Administration and Postgraduate Diploma in Management (PGDM) programs in India. In India, only two government bodies that certify full-time MBA institutions and their programs are the All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) and the University Grants Commission (UGC). The distance MBA has to be accredited by the Distance Education Council (DEC).
- Programs Full-time MBA programs:
This is normally completed in two years. Students may join this program after graduation or enter with work experience and take classes during weekdays like other university students. - Accelerated MBA programs:
This involves an increased course load with more intense classes and examination schedules, and is usually condensed into one year. They usually have less downtime during the course and between terms. Accelerated programs generally have lower fees than a full-time two-year program at the same business school. - Part-time MBA programs:
Generally, classes are on weekday evenings after office working hours, or on Saturdays and Sundays. Part-time programs may last two years or more. The students in these programs normally consist of working people, who take a less course load for a longer period of time. - Evening (second shift) MBA programs:
These are full-time programs that normally hold classes on weekday evenings, after office working hours, or on weekends for a duration of two years. The students in these programs generally consist of working professionals who cannot leave their jobs to pursue a full-time regular MBA. Most of the second shift MBA courses are offered at Business Schools in India. - Executive (part-time) MBA (EMBA) programs:
This course is developed to meet the educational needs of managers and executives, allowing students to earn an MBA/PGDM in two years or less while working full-time. Students come from every type and size of organization–profit, non-profit, government – representing a variety of industries. EMBA classes generally have a higher level of work experience, often 8 years or more, compared to other regular MBA students. Due to the increasing number of EMBA courses offered, the Executive MBA Council was established in 1981 to monitor and improve executive education. - Full-time executive MBA programs:
These are a new category of full-time 12 to 18 months Master of Business Administration programs aimed at working people with approximately 5 years or more of work experience. These are mainly offered in countries like India, where the 2-year MBA program is focused on freshers with no experience or minimal experience. - Distance learning MBA programs:
For this course, classes are held off-campus. This course is offered in different formats, through correspondence, email, non-interactive broadcast video, pre-recorded video, live teleconference or videoconference, offline, or online. Many Business schools offer these degrees now. - MBA dual degree programs:
This course combines with other programs, such as a BBA, B.Tech., MS, MA, etc., to let students cut costs (dual programs generally cost less than pursuing 2 courses separately). This also saves time on education and customizing the business education courses to their needs. This is generally completed by permitting core courses of one program to count as electives in the other. Few business schools/ universities offer five-year programs in which students can earn both a bachelor’s degree in business administration and an MBA.
Admissions & Selection criteria:
B Schools across the globe have different selection criteria, but mainly the following components are used in combination of undergraduate grade point average, academic transcripts, entrance examination scores, a resume containing significant work experience, essay writing, letters of recommendation, and a personal interview, which may be face-to-face or remotely through audio-video or by telephone. Some may also be interested in extracurricular activities, community service activities, or volunteer work, and how the student can improve the school’s diversity and contribute to the student body as a whole. For example, Taxila Business School takes only 10% weightage of entrance score.
The Graduate Management Admission Test is the most prominently used entrance exam for admission into Master of Business Administration programs internationally. The Graduate Record Examination (GRE) is also accepted by almost all MBA programs in order to fulfill any entrance exam requirement they may have. Some schools do not weigh entrance exam scores as heavily as other criteria, and some programs do not require entrance exam scores for admission. To have a diverse class, business schools may consider the target male-female ratio and local-international student ratios as well. In India, CAT, CMAT, MAT, ATMA, and XAT are the most popular entrance examinations.
In the requirements of the program, type and years of work experience can be a major admission component for some MBA degrees. Some top-tier Business Schools require five or more years of work experience.
Course Content
These programs are structured around the main core subjects, an essentially standard curriculum, and elective courses that will allow for a subject specialization or concentration. In the program’s first year (or part), students acquire both a working knowledge of management functions and the analytical skills required for these. In the second year (part), students pursue elective courses or specializations, which may count towards a specialization. After the first year, many full-time students need to take internships. A major project report or research report is usually a degree requirement after the completion of coursework. Many MBA programs end with a comprehensive end-of-year examination.
For EMBA, the main syllabus is mostly similar but may need to leverage the strengths of the more experienced and professional profile of the student, empowering leadership, and drawing more from the specific knowledge and experience of the individual students.
EMBA Programs are designed such that students gain exposure to theory and practice equally. The program may include lectures, case studies, and team projects; the mix, though, may differ by school and by format.
MBA Course Structure

Core MBA
- Analytical Skills: Accounting, economics (managerial economics, aggregate economics), organizational behaviour, quantitative analysis (operations research and business statistics).
- Functional Skills: human resource management, marketing management, operations management, and financial management.
- Ethics: Corporate governance, Business ethics, corporate social responsibility.
- Electives: The broad electives may include: entrepreneurship, international business, management information systems, business law, market research, organizational design, negotiations, international finance, project management, managing non-profits, and real estate investing. Many other elective options of a more specialized nature may be offered by different Business Schools.
- Capstone Strategy: Strategic management and business leadership, etc.
- Research: Research methodology and dissertation or a major project.
MBA Specializations/Concentrations:
- Accounting
- Entrepreneurship
- Finance (including corporate finance and investment management)
- International business
- Healthcare administration.
- Human resource
- Management information systems
- Management science
- Marketing
- Operations management
- Organizational design
- Project management
- Real estate
- Business Analytics
- Digital Marketing
- Design Thinking
- Risk management and strategy, among others.
Career in MBA

An MBA prepares students for different types of careers. According to a survey by the Graduate Management Admissions Council, 64% of MBA graduates used their MBA to change careers. A few of the general jobs an MBA prepares one for include:
- Business analyst or strategist
- Business development analyst, associate, or manager
- Market research analyst
- Managing Director (of a department)
- Investment banker
- Entrepreneur/founder
- Financial analyst, associate, or manager
- Management consultant
- Marketing associate, analyst, or manager
- Portfolio manager
- Project analyst or strategist
- Product analyst, associate, or manager
- Program analyst, associate, or manager
- Operations analyst, associate, or manager
- In InthereThere are many business schools and colleges offering two-year MBA or PGDM programs
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Taxila Business School
- Highest Placement Rs 28.60 Lakh / PA
- Average Placement Rs 11.5 Lakh / PA
- SpecializationTriple Specialization with Business Analytics compulsory.
- Ranking 10th All India.
- RatingAAA+
Read from Popular Posts:


